Use role-based access control (RBAC) and scope tags for distributed IT
Implementing, Transitioning or Transforming Microsoft Intune is more than just Turning The Service On? Just like all enterprise solutions, it needs a scalable solution so that the environment is maintained over time.
Now with scope tags and role-based access control you can make sure that the right administrators have the right access and visibility to the right Intune objects and resources all the time. Roles determine what access admins have to which objects. Scope tags determine which objects admins can see.
Let’s say a UK regional location admin has the Policy and Profile Manager role. You want this admin to see and manage only the profiles and policies that only apply to UK devices. To implement this type of access, following the below steps:
- Create a scope tag called UK.
- Create a role assignment for the Policy and Profile Manager role with:
- Members (Groups) = A security group named UK Admins. All admins in this group will have permission to manage policies and profiles for users/devices in the UK (Groups).
- Scope (Groups) = A security group named UK Users. All users/devices in this group can have their profiles and policies managed by the admins in the Members (Groups).
- Scope (Tags) = UK. Admins in the Member (Groups) can see Intune objects and resources that also have the UK scope tag.
- Add the UK scope tag to policies and profiles that you want admins in Members (Groups) to have access to.
- Add the UK scope tag to devices that you want visible to admins in the Members (Groups).
Note: Default Scope Tags
- The default scope tag is automatically added to all untagged objects that support scope tags.
- The default scope tag feature is similar to the security scopes feature in Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager.
Now lets create a scope tag
- In the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center, choose Tenant administration > Roles > Scope (Tags) > Create.
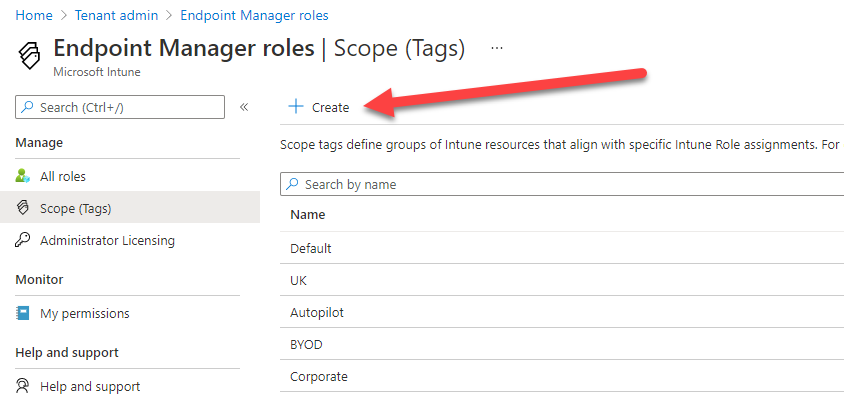
- On the Basics page, provide a Name and optional Description. Choose Next.
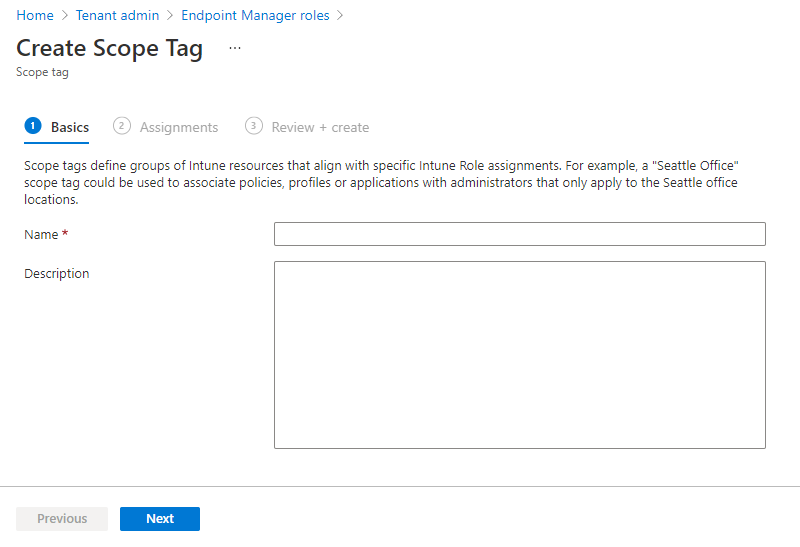
- On the Assignments page, choose the groups containing the devices that you want to assign this scope tag. Choose Next.
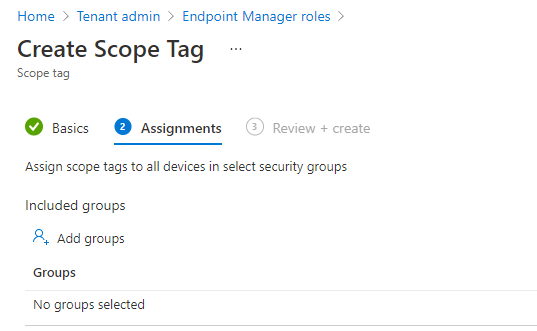
- On the Review + create page, choose Create.
Assign a scope tag to a role
- In the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center, choose Tenant administration > Roles > All roles > choose a role > Assignments > Assign.
- On the Basics page, provide an Assignment name and Description. Choose Next.
- On the Admin Groups page, choose Select groups to include, and select the groups that you want as part of this assignment. Users in these group will have permissions to manage users/devices in the Scope (Groups). Choose Next.
- On the Scope Groups page, select one of the following options for Assign to
- Selected groups: select the groups containing the users/deivces that you want to manage. All users/devices in the selected groups will be managed by the users in the Admin Groups.
- All users: All users can be managed by the users in the Admin Groups.
- All devices: All devices can be managed by the users in the Admin Groups.
- All users and all devices: All users and devices can be managed by the users in the Admin Groups.
- Choose Next
- On the Scope tags page, select the tags that you want to add to this role. Users in the Admin Groups will have access to Intune objects that also have the same scope tag. You can assign a maximum of 100 scope tags to a role.
- Choose Next to go to the Review + create page and then choose Create.
Now assign scope tags to other objects
For objects that support scope tags, scope tags usually appear under Properties. For example, to assign a scope tag to a configuration profile, follow these steps:
- In the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center, choose Devices > Configuration profiles > choose a profile.
- Choose Properties > Scope (Tags) > Edit > Select scope tags > choose the tags that you want to add to the profile. You can assign a maximum of 100 scope tags to an object.
- Choose Select > Review + save.
Tips! Scope tag details
When working with scope tags, remember these details:
- You can assign scope tags to an Intune object type if the tenant can have multiple versions of that object (such as role assignments or apps). The following Intune objects are exceptions to this rule and don’t currently support scope tags:
- Corp Device Identifiers
- Autopilot Devices
- Device compliance locations
- Jamf devices
- VPP apps and ebooks associated with the VPP token inherit the scope tags assigned to the associated VPP token.
- When an admin creates an object in Intune, all scope tags assigned to that admin will be automatically assigned to the new object.
- Intune RBAC doesn’t apply to Azure Active Directory roles. So, the Intune Service Admins and Global Admins roles have full admin access to Intune no matter what scope tags they have.
- If a role assignment has no scope tag, that IT admin can see all objects based on the IT admins permissions. Admins that have no scope tags essentially have all scope tags.
- You can only assign a scope tag that you have in your role assignments.
- You can only target groups that are listed in the Scope (Groups) of your role assignment.
- If you have a scope tag assigned to your role, you can’t delete all scope tags on an Intune object. At least one scope tag is required.
Multiple role assignments
If a user has multiple role assignments, permissions, and scope tags, those role assignments extend to different objects as follows:
- Assign permissions and scope tags only apply to the objects (like policies or apps) in that role’s assignment Scope (Groups). Assign permissions and scope tags don’t apply to objects in other role assignments unless the other assignment specifically grants them.
- Other permissions (such as Create, Read, Update, Delete) and scope tags apply to all objects of the same type (like all policies or all apps) in any of the user’s assignments.
- Permissions and scope tags for objects of different types (like policies or apps), don’t apply to each other. A Read permission for a policy, for example, doesn’t provide a Read permission to apps in the user’s assignments.